compile group: 'org.apache.ignite', name: 'ignite-core', version: '2.7.5'What is Apache Ignite?
Apache Ignite™ is a memory-centric distributed database, caching, and processing platform.
2 major use-cases
In-Memory Data Grid (IMDG)
In-Memory Database (IMDB)
In-Memory Data Grid
IMDG = Stores data (data grid) + Processes data (compute grid)
Stores entries in-memory
Data is distributed among nodes
May need external data source (DB, REST, other)
Collocated Processing = code goes to data
In-Memory Database
In Memory (or memory-centric) database
Ignite has Native Persistence since V2.1
Scalable: Each node stores only it’s own data part
Ignite can be used in combined mode (part of data is in-memory, part - persisted)
Why you may need Apache Ignite™
To speed up a slow traditional database by caching entries
To cache data from remote sources (REST, SOAP, any other network protocols)
For projects from scratch: Build a scalable solution with horizontal scaling
To remove a computational load from overloaded database
Avoid single point of failure by changing traditional database to cluster
Nodes
Apache Ignite cluster consists of two (major) type of nodes
Server node
Can store data
Can execute compute jobs
Usually, standalone JVM
Client node
Used to connect to the cluster
Setting up a project
Gradle
Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.ignite</groupId>
<artifactId>ignite-core</artifactId>
<version>2.7.5</version>
</dependency>Download full dirstibution
Go to Ignite Project site https://ignite.apache.org/ → Downloads → Binaries
Download latest binary release from the table here
Unzip to any folder.
\bin\ignite.sh / ignite.bat will start server node
Java Requirements
JDK 8 and later
Start script will auto-detect version of Java
Running using Java 9+ from IDE requires additional parameters
--add-exports=java.base/jdk.internal.misc=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-exports=java.base/sun.nio.ch=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-exports=java.management/com.sun.jmx.mbeanserver=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-exports=jdk.internal.jvmstat/sun.jvmstat.monitor=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-exports=java.base/sun.reflect.generics.reflectiveObjects=ALL-UNNAMED
--illegal-access=permit
Starting a server node
By default, Ignite starts server node
IgniteConfiguration cfg = new IgniteConfiguration();
try (Ignite ignite = Ignition.start(cfg)) {
System.out.print("Press any key to stop server.");
System.in.read();
}Starting client
Change configuration to start Ignite client
IgniteConfiguration cfg = new IgniteConfiguration();
cfg.setClientMode(true);
try (Ignite ignite = Ignition.start(cfg)) {
}Both server and client nodes will log
Topology snapshot [ver=2, locNode=b5fc314f, servers=1, clients=1, state=ACTIVE, CPUs=12, offheap=3.2GB, heap=7.1GB]
This means nodes detected each other
Save data into Grid
Ignite supports JCache JSR 107 API,
IgniteCache<K,V> extends javax.cache.Cache<K,V>
IgniteCache<Integer, String> cache = ignite.getOrCreateCache("myCacheName");
// Store keys in cache (values will end up on different cache nodes).
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
cache.put(i, Integer.toString(i));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
System.out.println("Got [key=" + i + ", val=" + cache.get(i) + ']');Dynamic Cache
ignite.getOrCreateCache(CacheConfiguration cfg)
Creates an instance of the cache on the fly
ignite.createCache(CacheConfiguration cfg)
Creates cache instance
Ignite will create and deploy the cache across all server cluster members
Cache will be deployed to any new joined node
Limitation - not possible to create new cache in transaction
Static cache
Accessed using method
ignite.cache(String name)
Will return existing cache or null
No cache creation under running transaction
User has to provide configuration before node startup
Application and cache
Applications are usually made up of multiple caches
one for each data type to be stored
— This is a best practice
— If you have two classes, Card and Client, you should have two caches
Replicated and partitioned
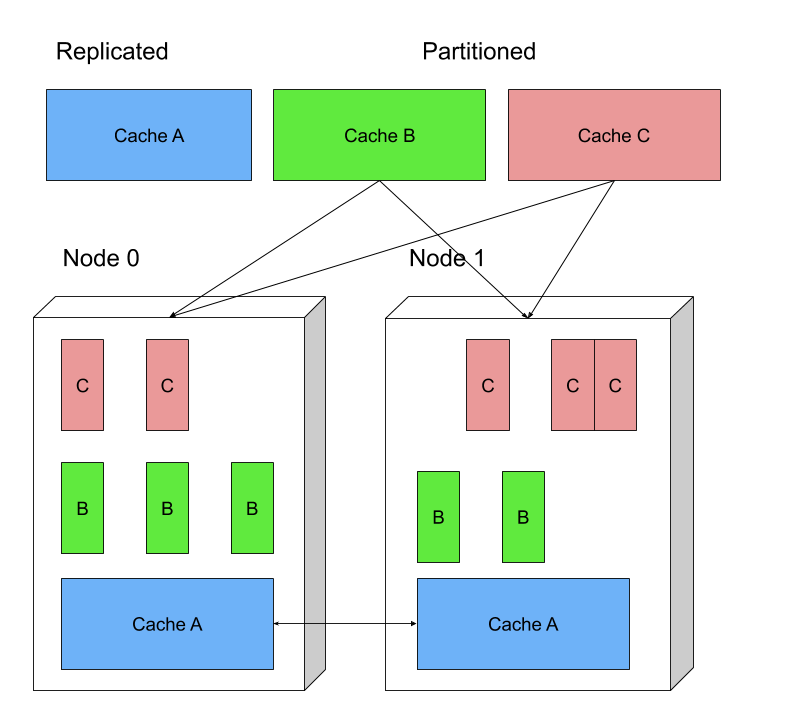
Replicated - Cache A Partitioned - Cache B & C Replicated, use case: rare write, often - read, e.g. dictionary
Partitioned Caches
Most common usage of cache
1024 partitions
No redundancy
In-memory - volatile
Warning | Configure backups for fault tolerance |
For most cases: 1 backup is enough
Cache Atomicity Mode
ATOMIC
distributed transactions not supported; distributed locking not supported
higher performance and throughput ratios
TRANSACTIONAL
ACID Compliant
Transaction over several caches requires all caches to be transactional
TRANSACTIONAL_SNAPSHOT
ACID for SQL Queries
Non SQL query Scan query
Provides iteration over cache data
May have additional filter
Filter is sent to server
Iterator over cache uses scan query
Scan query example
IgniteBiPredicate<Long, Customer> filter
= (Long k, Customer v) -> v.email != null && v.email.contains("@test.com");
try (QueryCursor<Cache.Entry<Long, Customer>> cursor
= cache.query(new ScanQuery<Long, Customer>().setFilter(filter))) {
for (Cache.Entry<Long, Customer> entry : cursor.getAll())
System.out.println(entry.getValue().name + " " + entry.getValue().phoneNumber);
}SQL support
Provides full ANSI SQL-99 support including
aggregations
distributed joins
Drivers
JDBC
ODBC
DML: SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE queries & subset of DDL
SQL in Apache Ignite
H2 In memory SQL database part of Ignite process
parse/execute query
not storage
Additional module 'ignite-indexing' is required in the classpath of all Ignite nodes.
Adding indexing module
Gradle
compile group: 'org.apache.ignite', name: 'ignite-indexing', version: '2.7.5'Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.ignite</groupId>
<artifactId>ignite-indexing</artifactId>
<version>2.7.5</version>
</dependency>Declare cache visible as table
CacheConfiguration<Long, Customer> ccfg = new CacheConfiguration<>("customer");
ccfg.setQueryEntities(Collections.singletonList(new QueryEntity(Long.class, Customer.class)));Otherwise:
IgniteSQLException: Failed to find SQL table for type: Client
Declare visible entity fields
@QuerySqlField
private String email;
@QuerySqlField(index = true)
private String phoneNumber;email is declared to be visible by SQL engine
phoneNumber is declared as visible and index build is required
SqlQuery
Result is a number of Java objects (entries)
Only filter condition is specified by user
"Select * from Customer" is always added automatically
Table name based on entry class name
SqlQuery Example
String phoneNum = "+1-541-754-3010";
try (QueryCursor<Cache.Entry<Long, Customer>> qry
= cache.query(new SqlQuery<Long, Customer>(Customer.class, "where phoneNumber = ?")
.setArgs(phoneNum))) {
for (Cache.Entry<Long, Customer> entry : qry) {
Customer val = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Customer found " + val);
}
}SqlFieldsQuery
"Projection" of entry
Result is List<?> - fields
Subset/specific fields
Full SQL statement is required
SqlFieldsQuery Example
SqlFieldsQuery qry = new SqlFieldsQuery("select concat(name, ' <', email, '>') from Customer");
// Execute query to get collection of rows. In this particular
// case each row will have one element with full name formatted in Git-style
Collection<List<?>> res = cache.query(qry).getAll();
// Print names.
System.out.println("Names of all customers:" + res);